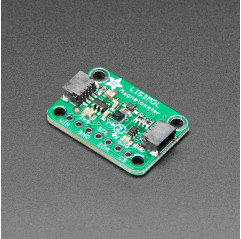
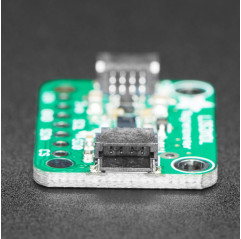
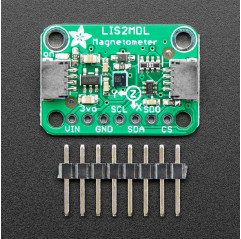
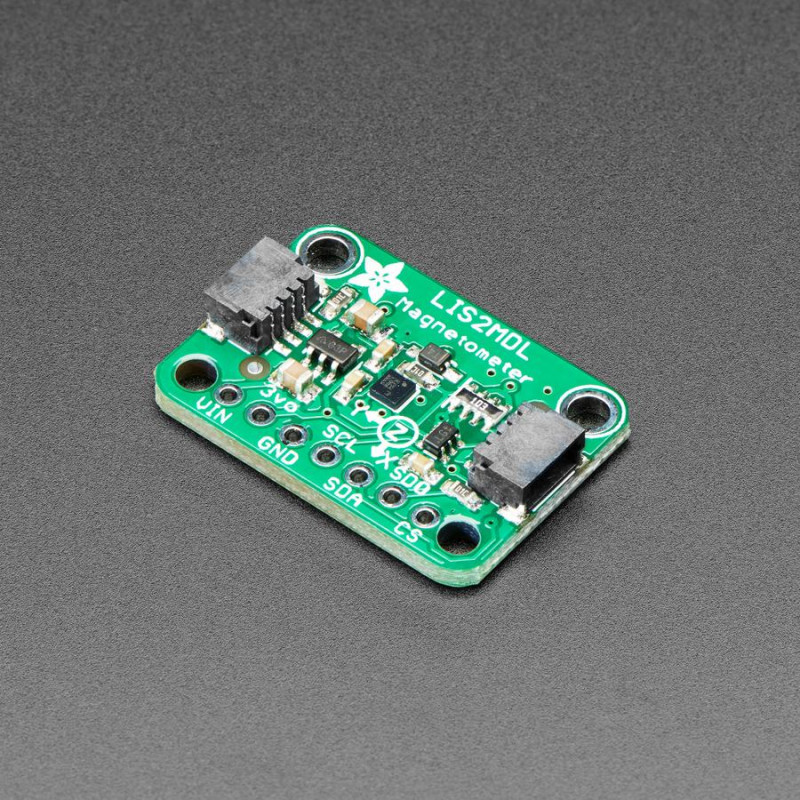
Sense the magnetic fields that surround us with this handy triple-axis magnetometer (compass) module.
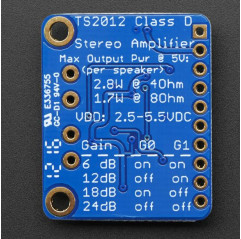
Magnetometers can sense where the strongest magnetic force is coming from, generally used to detect magnetic north, but can also be used for measuring magnetic fields. This sensor tends to be paired with a 6-DoF (degree of freedom) accelerometer/gyroscope to create a 9-DoF inertial measurement unit that can detect its orientation in real-space thanks to Earth's stable magnetic field. It's a great match for the LSM6DSOX from ST!Adafruit based this breakout on ST's LIS2MDL, a great general purpose magnetometer with a very wide range and bot I2C and SPI interfaces. This compact sensor uses I2C to communicate and it's very easy to use. Simply download the library and connect the SCL pin to your I2C clock pin, and SDA pin to your I2C data pin and upload our test program to read out magnetic field data. If you'd like, you can also use SPI to receive data (we just happen to prefer I2C here)
This sensor can sense ranges from +-50 gauss (+- 5000 uTesla!) with no range-setting required. For high resolution, you can read at 100 Hz update rate. If you don't mind a little loss of precision, the sensor can output at 150 Hz.
To make life easier so you can focus on your important work, Adafruit have taken the LIS2MDL and put it onto a breakout PCB along with support circuitry to let you use this little wonder with 3.3V (Feather/Raspberry Pi) or 5V (Arduino/ Metro328) logic levels. Additionally, since it speaks I2C you can easily connect it up with two wires (plus power and ground!). They've even included SparkFun qwiic compatible STEMMA QT connectors for the I2C bus so you don't even need to solder! Just wire up to your favorite micro and you can use CircuitPython/Python or Arduino drivers to easily interface with the LIS2MDL and get magnetic measurements ASAP.
It's fully assembled and tested. Comes with a bit of 0.1" standard header in case you want to use it with a breadboard or perfboard. Four 2.5mm (0.1") mounting holes for easy attachment.
Code, schematics, wiring diagrams, Arduino and Python examples are all in the Learning System guide
TECHNICAL DETAILS
Code, schematics, wiring diagrams, Arduino and Python examples are all in the Learning System guide
Technical Specifications:
Fixed I2C address 0x1E or SPI data mode
±50 gauss magnetic fixed full scale
Max 150 Hz update rate
Continuous and single-conversion modes
16-bit data output
Interrupt data pin in I2C mode
Self-test mode