We conclude our little glossary of 3D printing with these last words. So many other terms have not been mentioned, but in getting into this technology as we go along they will all become a little more understandable.
R
Raft: a thickness of layer outside the base of the object that is added to limit the likelihood of warping.
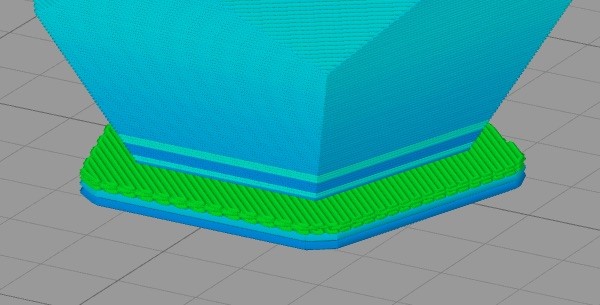
Raft - source simplify3d
Rapid prototyping: the process of creating physical prototypes directly from digital data.
Reverse engineering: creating a digital representation of a physical object to define its shape, size, interior and exterior. Then realized by additive manufacturing.
Flexural strength: the stress (in MPa) at failure in bending.
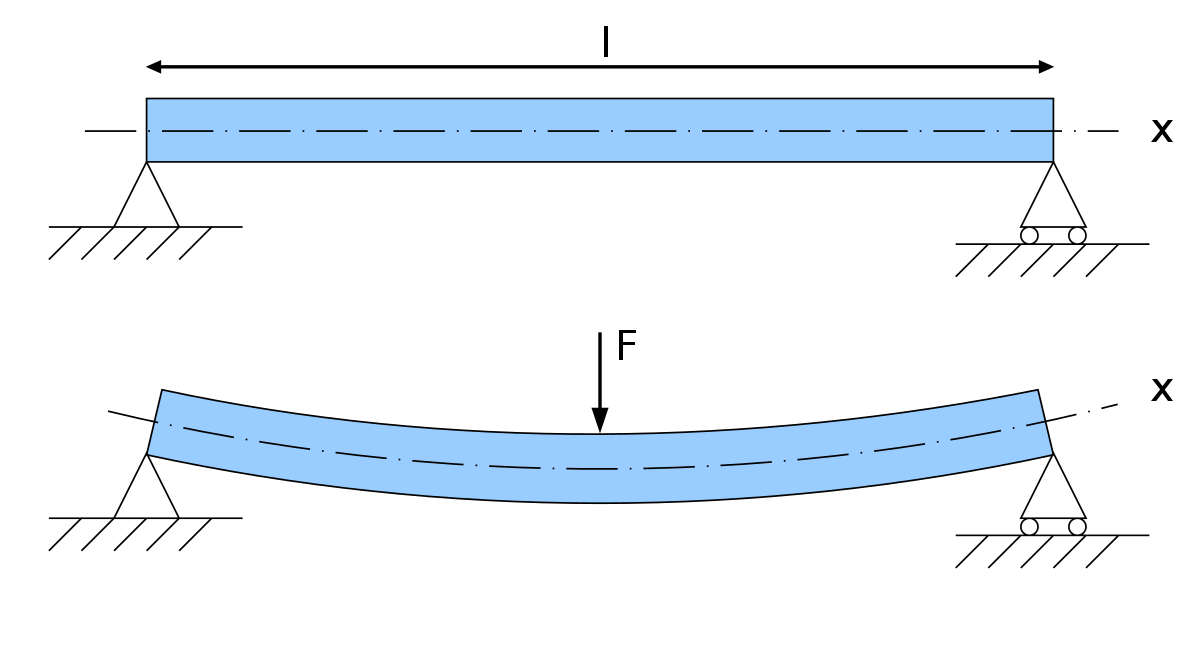
Flexure (mechanical) - source Wikipedia
Tensile strength: the stress (stated in MPa) at which a material fractures or breaks when subjected to a tensile load.
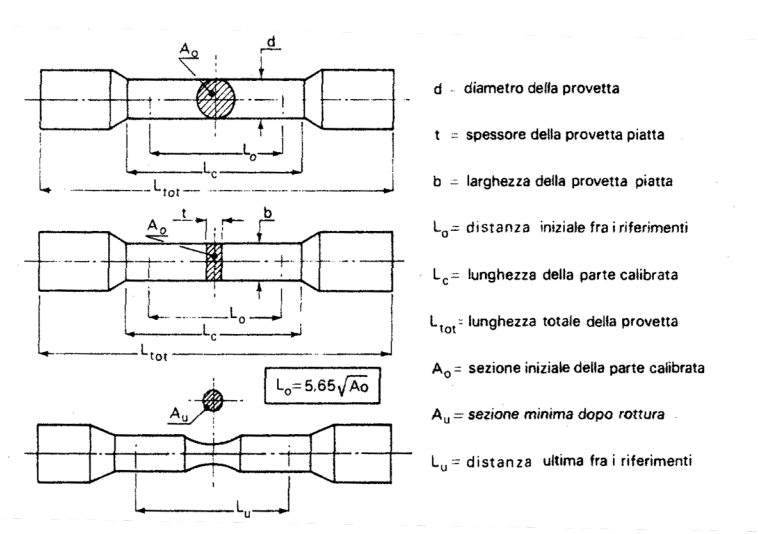
Tensile strength - source: Ballio, Mazzolani. Steel structures
Filling: usually represented as a percentage is a value that shows how much a solid model should be filled with the molded material. 100% fill means that the part is completely filled. Different filling is used to make 3D printing cheaper and faster.
Print resolution: refers to the height of layer used for a 3D print. The lower the height of the build layer, the higher the resolution of the final object.
S
3D scan: a process that captures the geometry of a real object and uses that data to produce a 3D model.

Large-format 3D scanning with photogrammetry - source Shining3D
Sintering: the process of melting particles to form a solid mass of material using heat or pressure without melting it.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS®): an additive process by which metal objects are constructed, directly from files CAD. Parts are built layer by layer by local laser melting of metal powders with a very fine grain size such that they can be built with layer down to 20 microns.
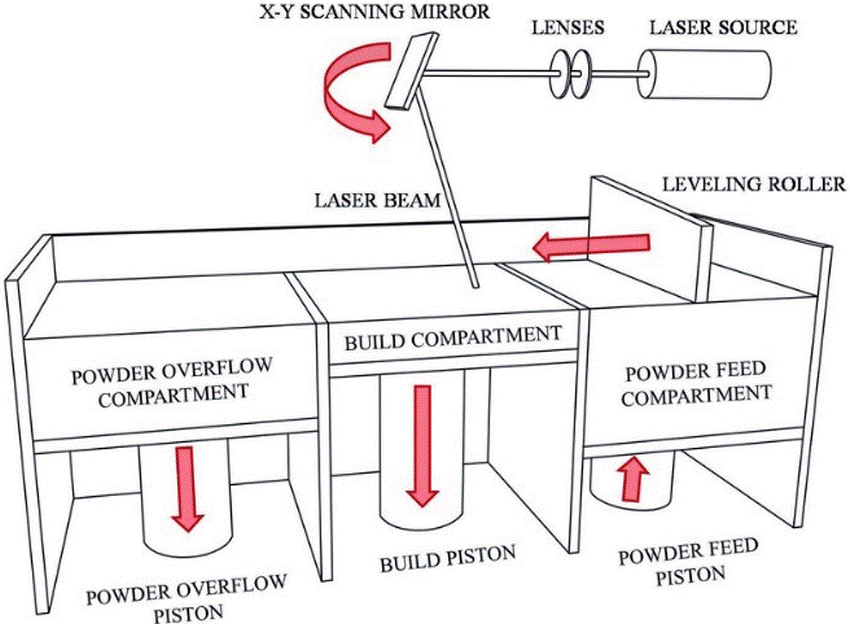
DMLS 3D printing process - source DOI:10.5772/intechopen.89804
Additivesystems: machines used for additive manufacturing.
Skirt: a layer external to the base of the object, but not attached, used to clean the nozzle head.
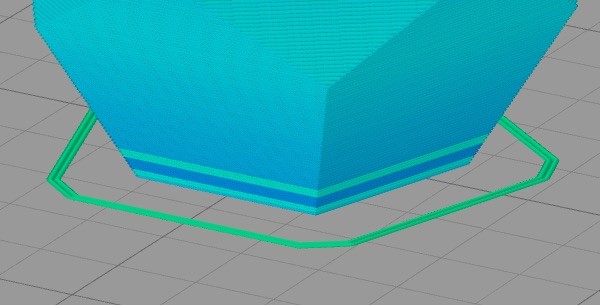
Skirt - source simplify3d
SLA: stands for stereolithography, a process that creates 3D prints from a liquid (photopolymer) resin by solidifying the material layer by layer using a laser.
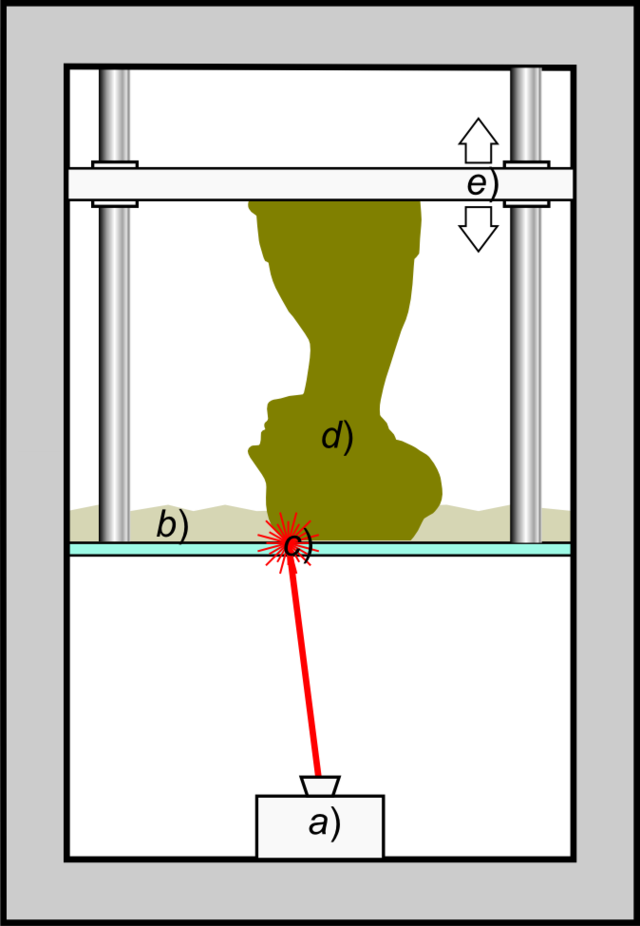
Stereolithography - source Wikipedia
SLS: short for Selective Laser Sintering, uses a laser to shape and form extremely thin layers of powdered material by fusing or sintering them one layer at a time to create a solid structure.
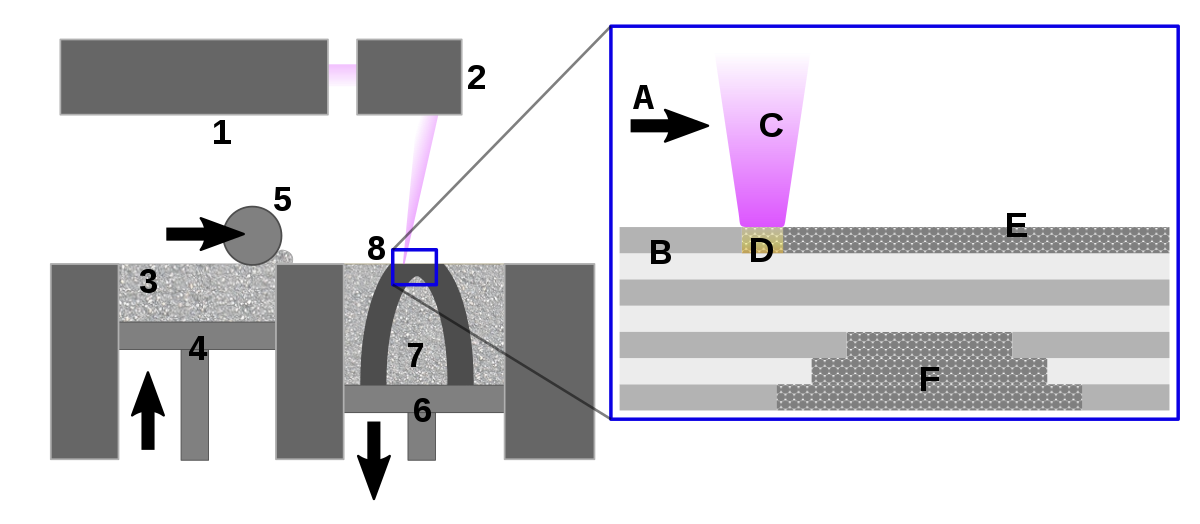
Selective Laser Sintering - source Wikipedia
3D printing: the act of using an additive manufacturing machine (3D printer) to produce a solid object one layer at a time (also sometimes called as additive manufacturing).
Hollow printing: a 3D print that is not solid and contains no filler. Hollow models are much faster and cheaper to print but have very low strength.
Injection molding: the process of injecting molten liquid plastic into a mold. The plastic fills empty cavities in the mold and as it cools it solidifies. This finished part is then ejected from the mold and the process is repeated again.
3D printer: an additive manufacturing machine that builds a solid shape by constructing one layer at a time.
STEP (STandard for the Exchange of Product model data - "Standards for Product Data Exchange"): is a standard containing a set of rules for the integration, presentation and exchange of data (via computer). It can be used to transfer data between the following systems: CAD, CAM.
STL (STereo Lithography interface format or acronym for "Standard Triangulation Language"): is a file format, binary or ASCII, that originated for stereolithography software CAD. It is used in rapid prototyping (rapid prototyping) through software CAD.
Support: is the additional material printed during a 3D print that enables successful printing of a design with complex geometries. Support is needed to successfully print overhangs and bridges and is removed and discarded in post-processing.
T
Tank (or reservoir): indicates the area where the resin is located before being cured in the SLA process.

Example of Resin tank - source Formlabs
Glass Transition Temperature: the temperature range at which a material transitions from a hard, glassy consistency to a fluid consistency.
Print time: indicates the total time it takes for a 3D printer to complete making the chosen object.
Thermoplastic: a plastic material that becomes flexible or moldable above a specific temperature and solidifies after cooling.
Printhead: the part of a 3D printer where the material is extruded.
U
Nozzle (nozzle): the part of a 3D printer from which the build material is extruded.

Nozzle various models - source e3D
V
Print speed: the speed at which the print head moves, usually measured in mm / s.
Print volume: the maximum possible size on which a 3D printer can print.
W
Wall thickness: the wall thickness, generally associated with the minimum thickness, i.e., the thinnest size that can be printed so that the model does not collapse. It varies by technology.

Wall Thickness - Formlabs source.
Warping: a defect in 3d printing. The warping occurs when an object cools after printing. The cooling causes a contraction, and this contraction causes stress along the side surfaces of the object. The more rapido the cooling, the greater the stress on the object.
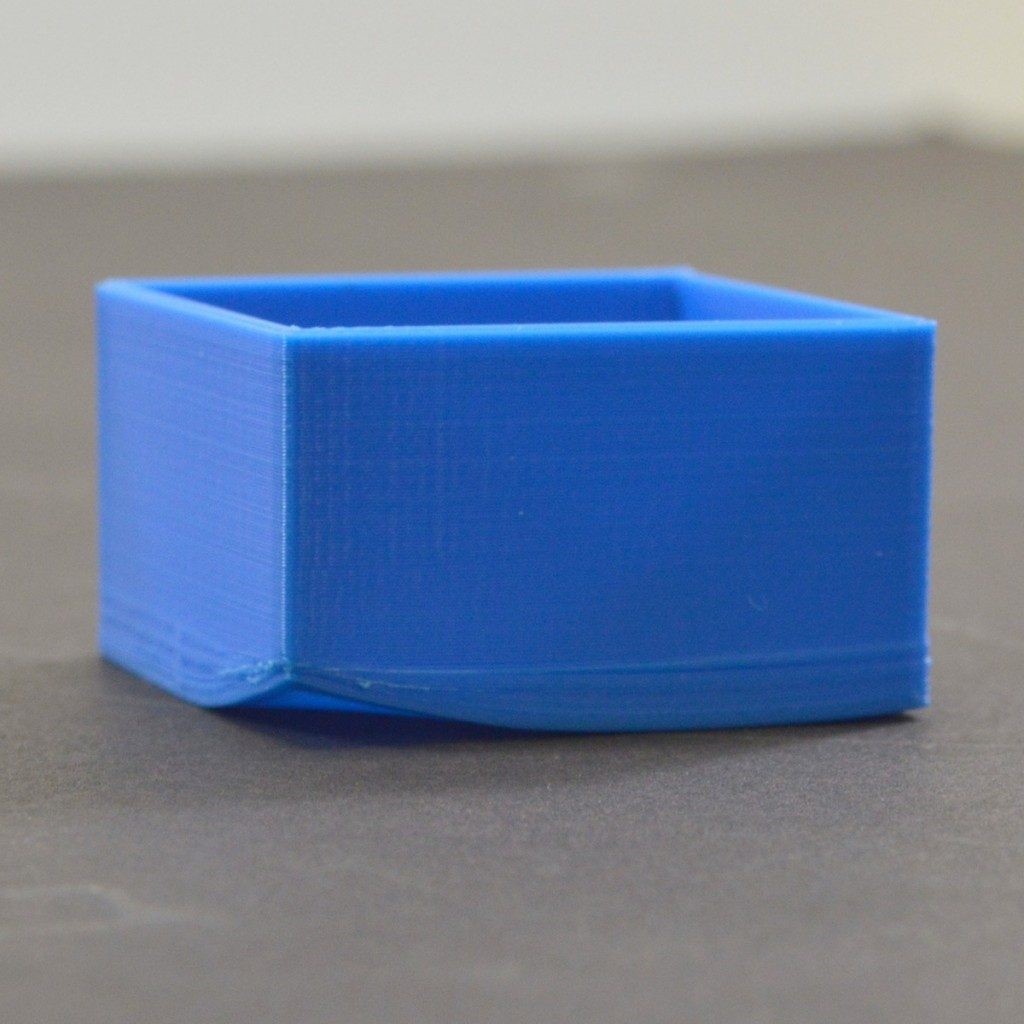
Warping - source Simplify3D
Need technical support?
If you need more information CONTACT US
Follow our social media to stay up to date with news!







