When entering the world of 3D printing you will encounter many new technical and specific terms. So to start with the basics here you can find a glossary of the most common words used in the field of 3D printing - part one.
A
ABS: acronym for acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene, a thermoplastic polymer commonly used in FDM 3D printing.
Acetone: is a solvent used as a smoother in post-processing of 3D printed ABS parts.
Additive manufacturing (AM): a process of joining materials to create objects from 3D model data, usually on a layer, as opposed to subtractive manufacturing methodologies. Synonyms: additive manufacturing, additive processes, additive techniques, additive layer production.
Height layer: Also called "print resolution," this is the height of each layer of a 3D print, it is measured in microns (µm). The height of layer is the main factor affecting both printing time and vertical resolution. Choosing thicker layers can reduce printing time at the cost of more visible layers. On the other hand, choosing thin layers (e.g., 0.10 mm) will result in better detail at the cost of longer printing time.
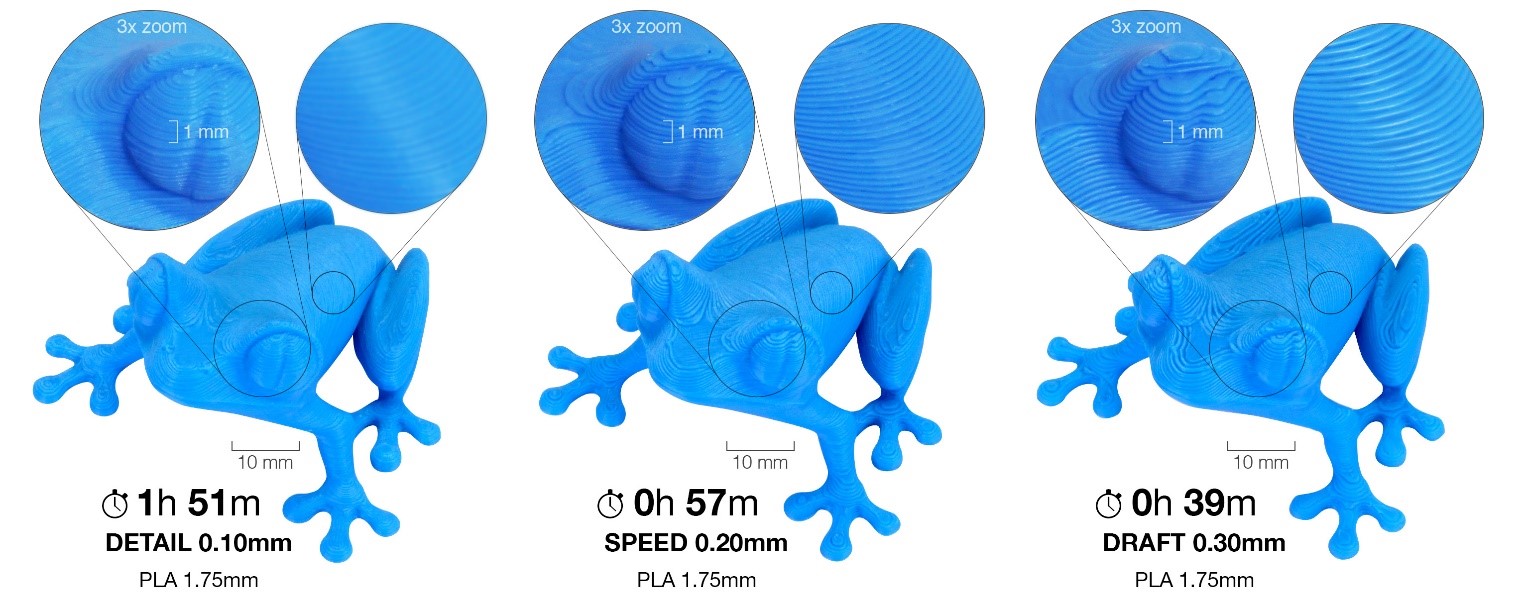

Height layer - source PrusaSlicer
Amorphous: any non-crystalline solid in which atoms and molecules are not organized in a defined lattice pattern. Glass and polymers are typical amorphous solids. Opposite of crystalline.
Anisotropic: material that has varying physical properties when measured in different directions. Wood and composite materials are common examples of anisotropic materials. Opposite of isotropic.
X-axis: the direction from side to side (left and right) relative to the printing plane
Y-axis: the direction from back to front relative to the print bed.
Z axis: the up and down direction relative to the printing bed.
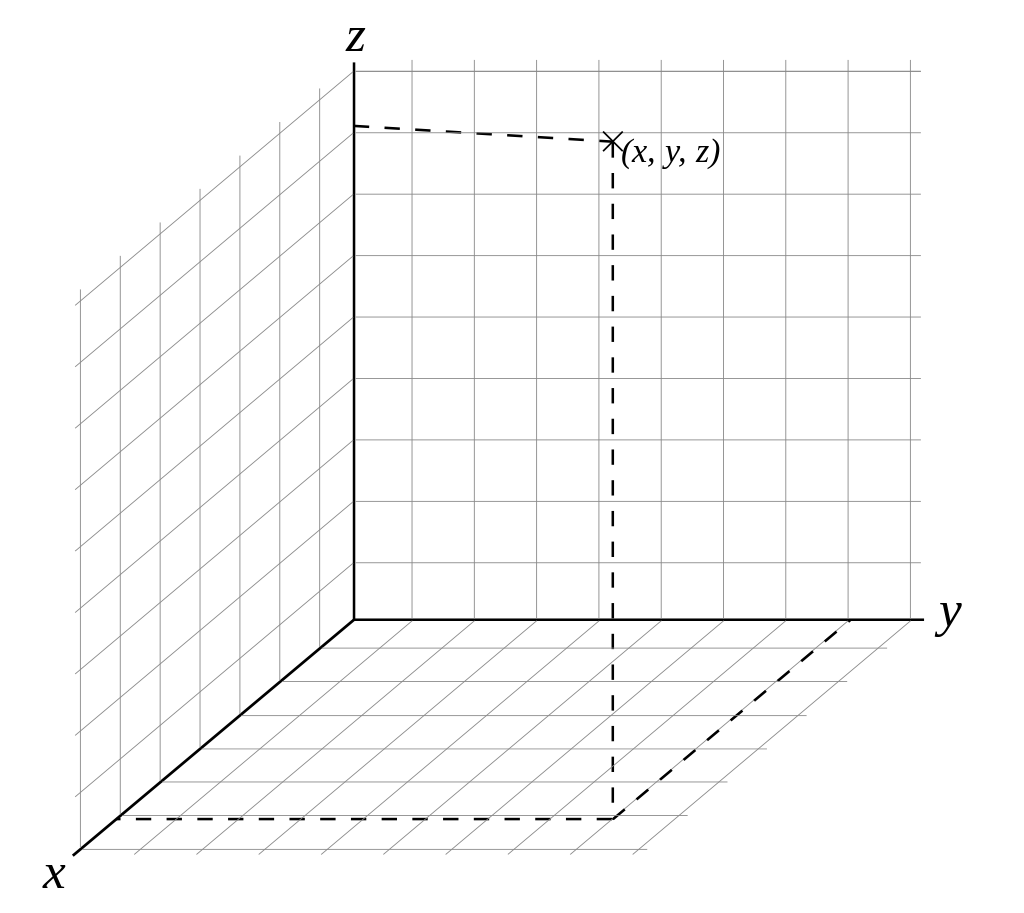
Three-dimensional Cartesian reference system - source Wikipedia
B
Binder jetting: is a printing method that uses thin layers of powder to build a 3D model. The powder is bound by a binding agent that allows the object to solidify. After the printing process, models are reinforced with superglue and UV coating to prevent discoloration from sunlight.
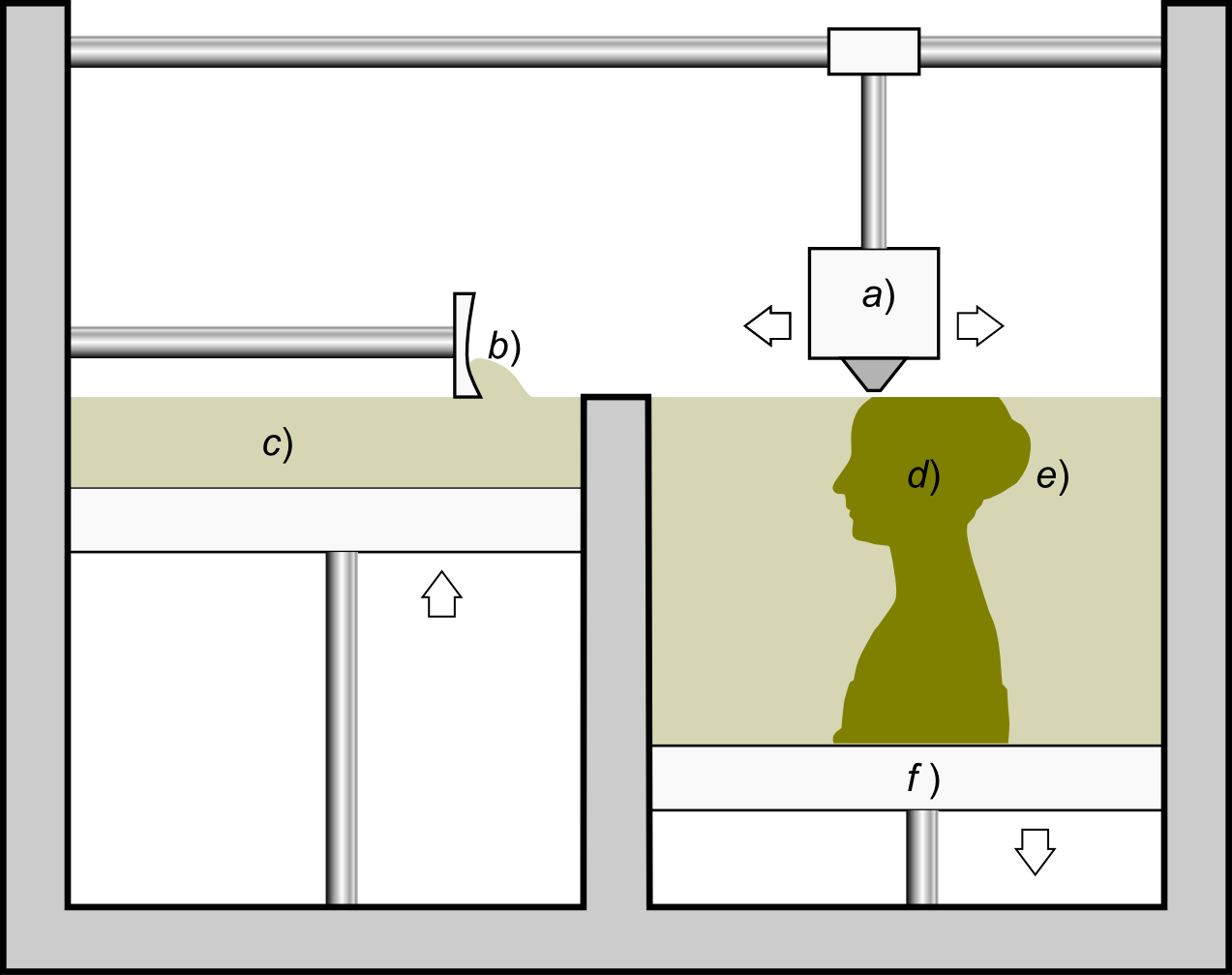
Schematic representation of a 3D printer using Binder Jetting technology - source Wikipedia
Brim: indicates a single flat layer printed around the base of a model to prevent deformation. The edge width can typically be changed in a slicer program.
Brim - PrusaSlicer source.
Bridge: a phenomenon that occurs when printing involves a bond between 2 supports or anchor points, without underlying supports.
C
CAD (Computer Aided): a design method in which a computer program is used to create 3D objects in the form of electronic files.
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing): typically refers to systems that use surface data to drive CNC machines.
CNC: computer numerically controlled machining, a subtractive manufacturing method involving a computer-controlled machine that removes material on a predetermined path to produce a final object.
Creep: the tendency of materials to move or deform over time when subjected to continuous loading. Resins and polymers often exhibit this phenomenon.
Crystalline: any solid in which atoms and molecules are organized in a lattice pattern. Metals are crystalline solids. Opposite of amorphous.
D
Deformation: due to the high heat involved in most of the 3D printing process, differential cooling results in printing cooling areas at different rates resulting in deformation.
Nozzle diameter: the diameter of the material being extruded from the nozzle.
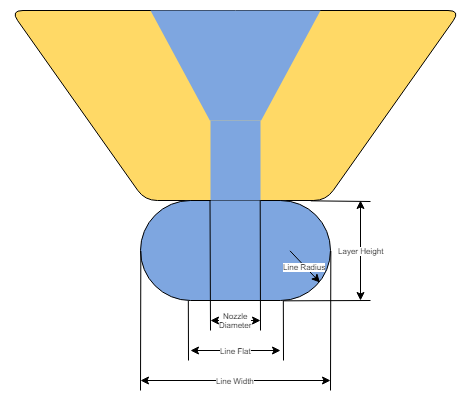
Section of a nozzle extruding a plastic line - source Dyze Design
Ductility: a material is said to be ductile if it can deform without losing strength. Opposite of brittle.
E
Extruder: The extruder takes filament from the spool, melts it and pushes it through a nozzle onto the build plate.
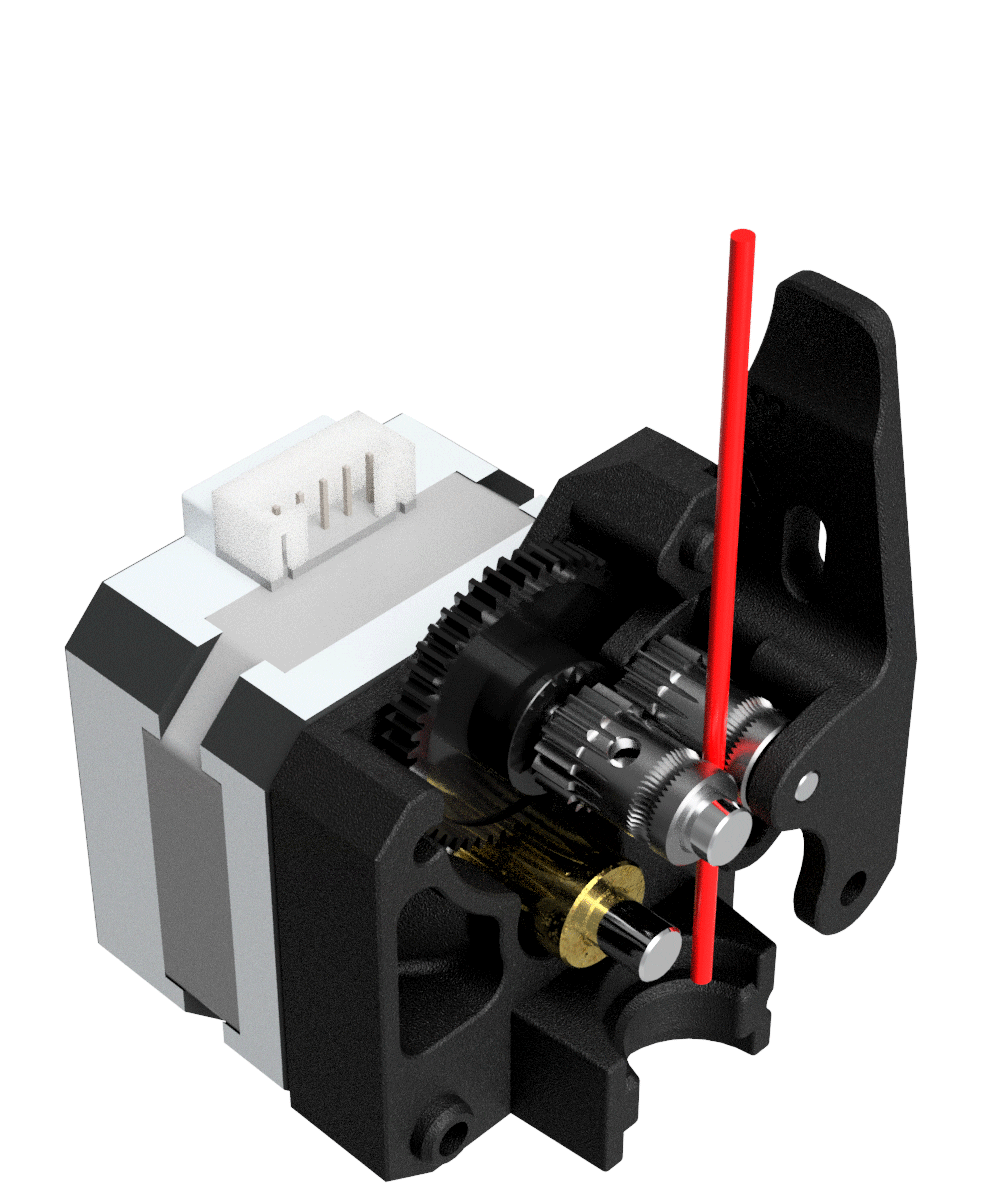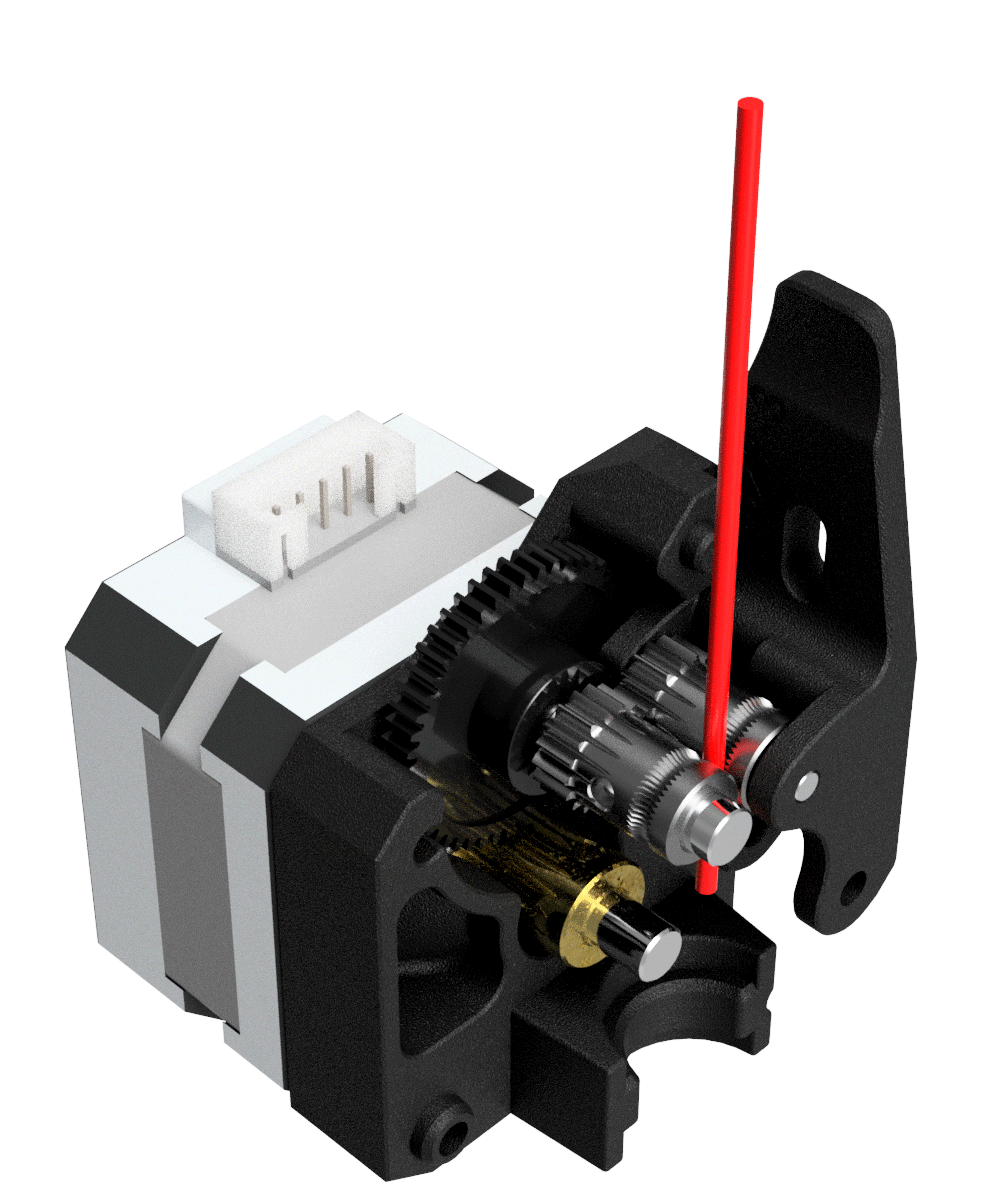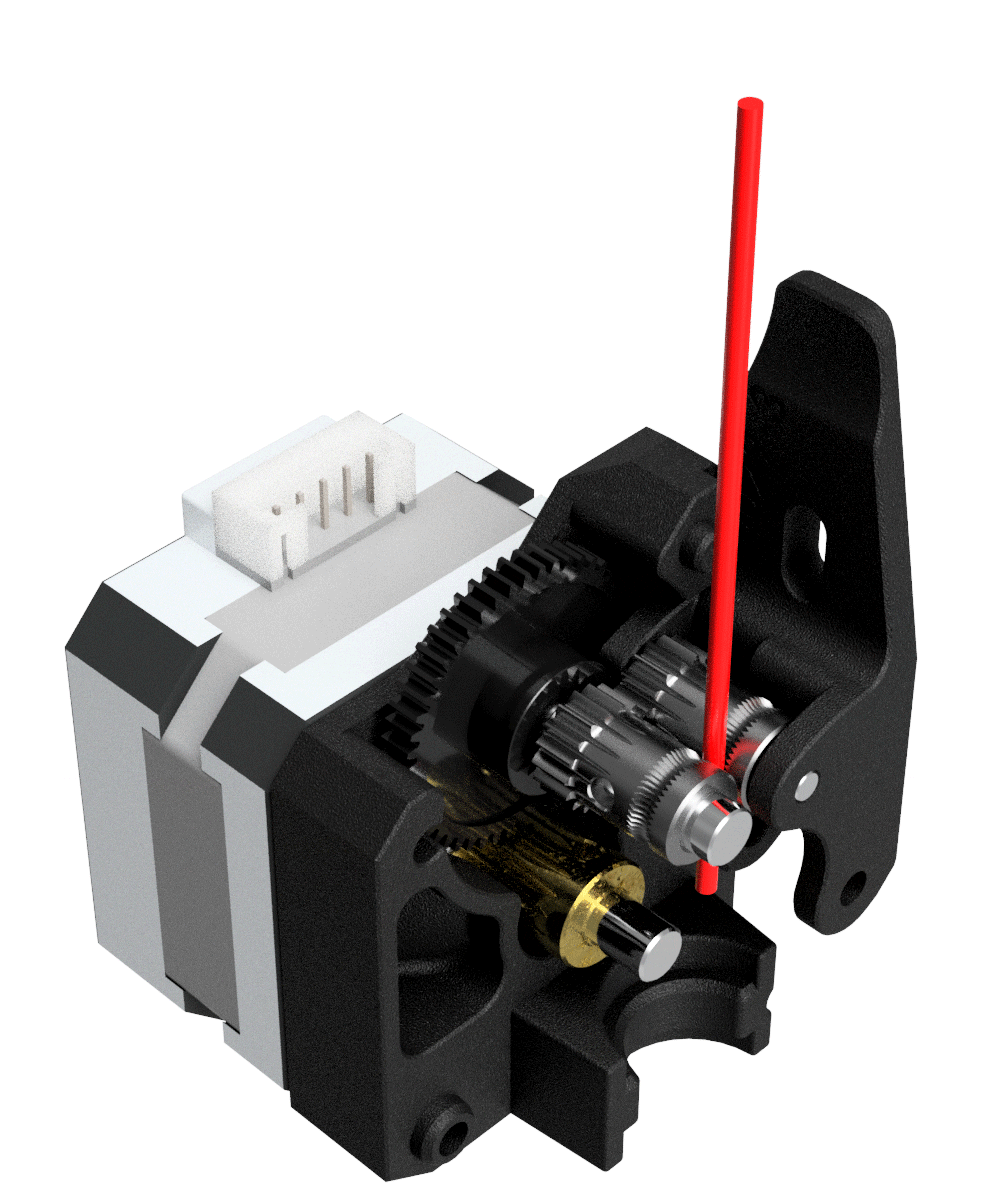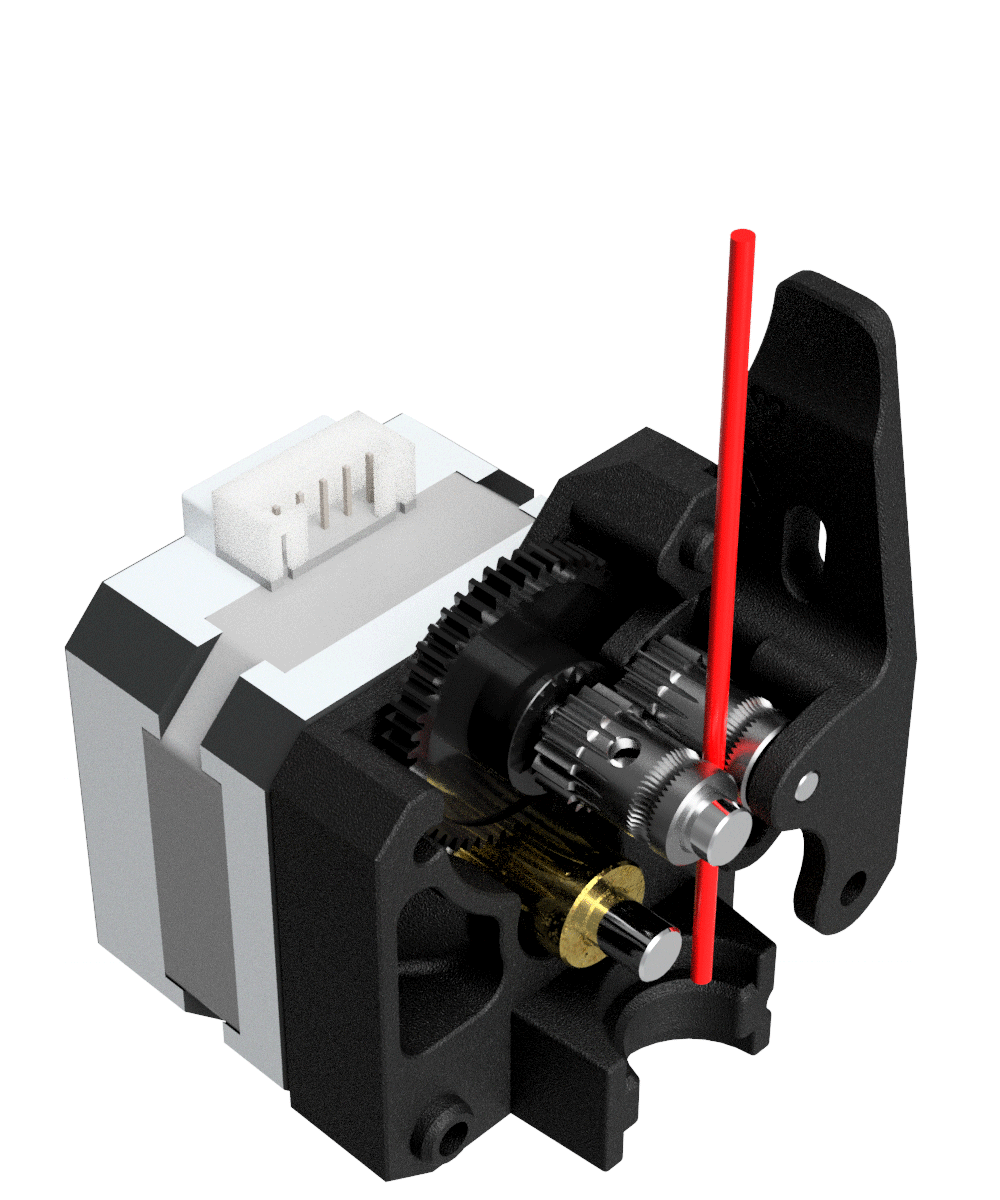
X-Ray View Of Bondtech Mini Geared BMG - source. Bondtech
Do you need technical support?
If you need more information CONTACT US.
Follow our social media to stay up to date with the latest news!







