We continue with a small glossary of 3D printing: part two.
F
Facet: typically a three- or four-sided polygon representing an element of a 3D polygonal surface or mesh model. Used for creating files STL.
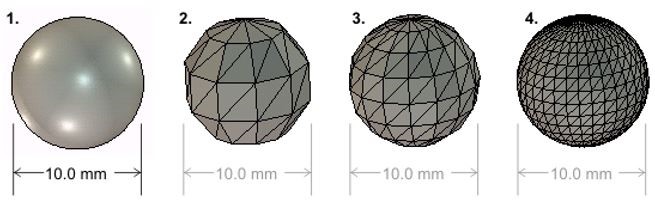
Example of different resolutions for files STL - source SOLIDWORKS
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): uses a string of solid material (filament), pushing it through a heated nozzle and melting it in the process. The material is deposited at a specific point where it cools instantly and solidifies. This builds the model layer by layer. This is the most common 3D printing technology.
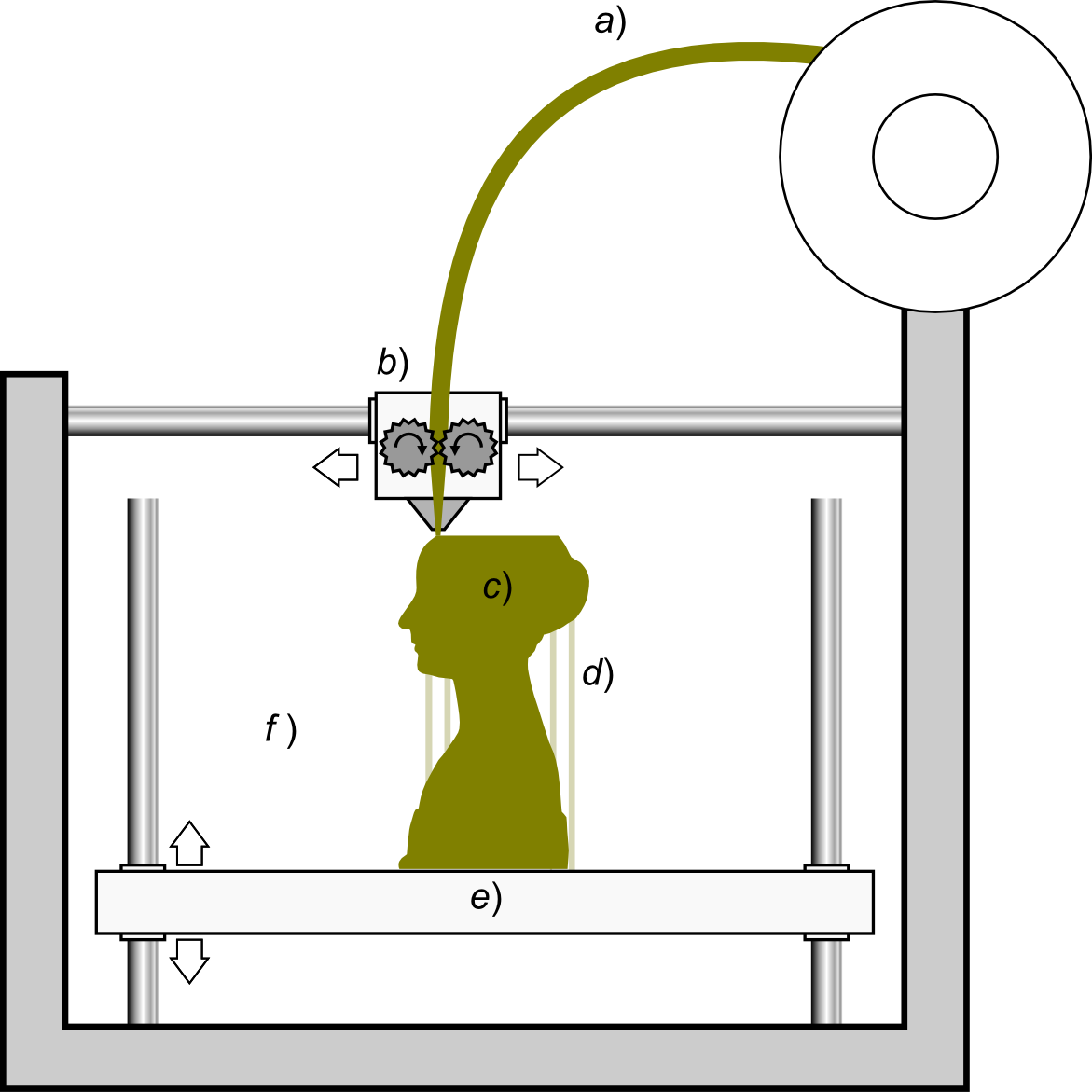
FDM fused deposition modeling - source Wikipedia
Filament: the general term given to the material used in FDM printing. It is usually supplied in spools or rolls, and the filament is heated and extruded through the nozzle that deposits it on the print bed.
File OBJ: A geometry definition file. The patterns CAD are exported as a file OBJ and then imported into a slicer program. The slicer program then converts the file to G-code to be interpreted by the 3D printer. Similar to the .STL files.
STL file : a geometry definition file that uses triangles to describe the surfaces of a 3D model. The CAD models are exported as a STL file and then imported into a slicer program. The slicer program then converts the file to G-code to be interpreted by the 3D printer.
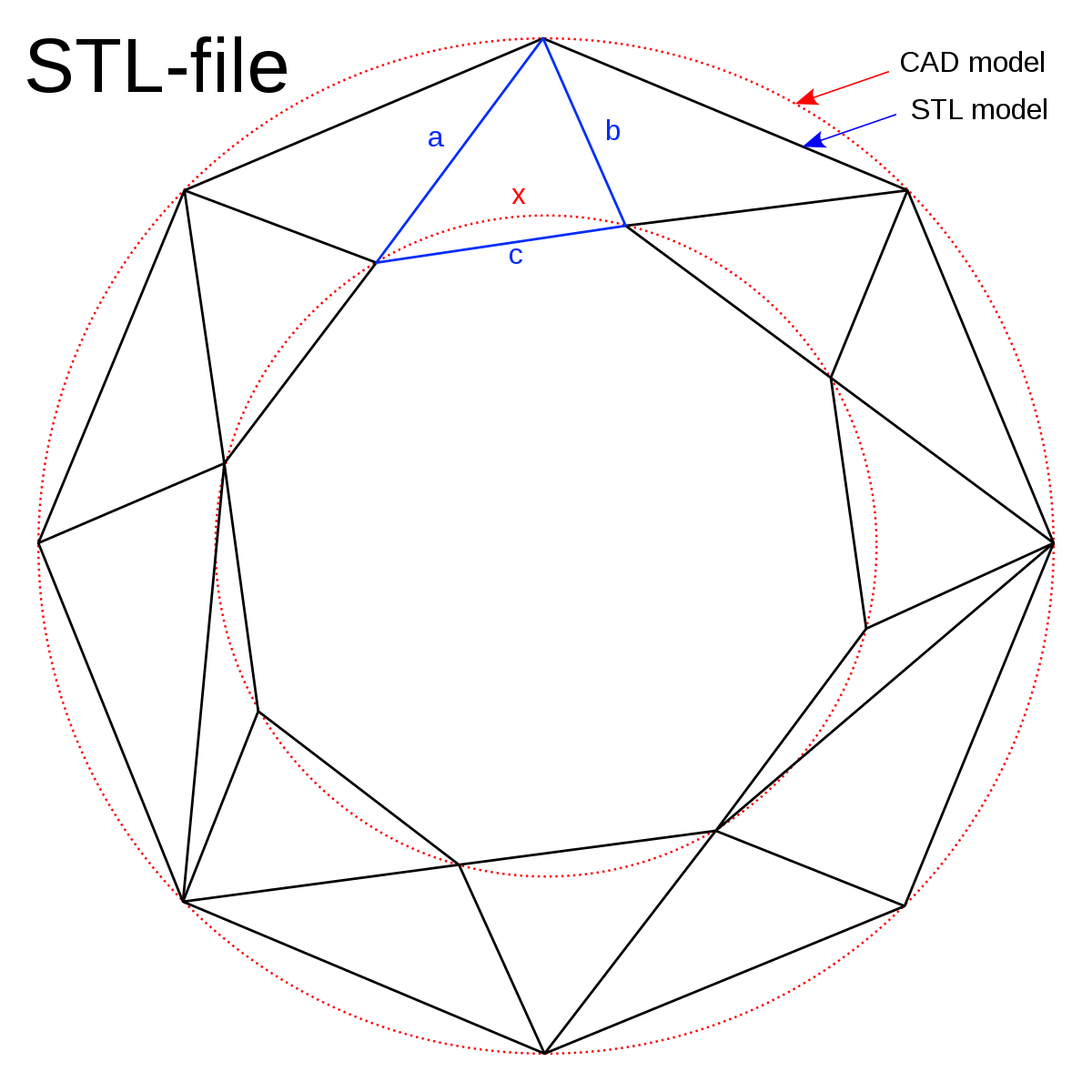
STL (file format) - source Wikipedia
Photopolymerization: an additive manufacturing process in which liquid photopolymer in a tank is selectively affected by light-activated polymerization.
Photopolymer: a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light.
Brittleness: characteristic of materials that break without undergoing significant deformation. Examples include gypsum and ceramics.
Melting (casting): the process of pouring a liquid material (typically molten metal) into an empty cavity to produce a solid object of a specific shape when the liquid hardens.
G
G-code: denotes the most widely used numerical control (NC) programming language. It is used in computer-aided manufacturing to control automated machine tools (such as 3D printers and CNC machines).

Example of the central body of a G-code - source DOI:10.1145/3264918
H
Home: is the initial position of the 3D printer axes. For an FDM 3D printer, it is the mechanical position X = 0, Y = 0, Z = 0.
Hotend: the melter, is the hot body where the filament for FDM 3D printing is melted.
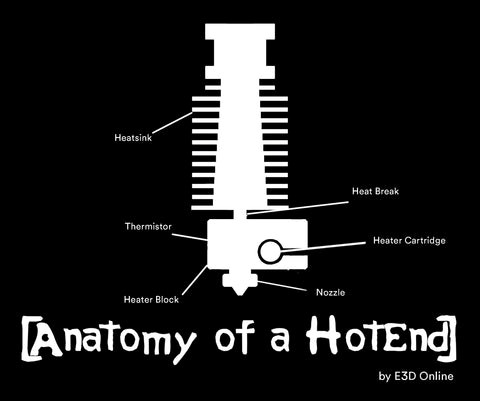
Example of hotend - source e3D
I
Curing (curing): refers to the curing of resin or photopolymers used for 3D printing, typically this step is performed with UV light.
Islands: a phenomenon that occurs in SLA printing that refers to cross sections of a model that are not connected.
Isotropic: a material that has the same physical properties in all directions. Glass and metal are common examples of isotropic materials. Opposite of anisotropic.
IGES (Initial Graphics Exchange Specification): a data exchange format platform CAD intended for the exchange of product geometry data.
J
Jig (jig): this is a frame used to hold components or parts in a fixed position, it is usually used in the assembly or manufacturing process.
L
UV light: in 3D printing refers to the type of light that is used to cure (harden) photopolymers in 3D printing SLA and Polyjet.
M
3D modeling: the act of using CAD 3D programs to produce a design.
3D model: a 3D design produced with a program CAD.
Fused deposition modeling (FDM®): material extrusion process used to make thermoplastic parts by heating, extruding, and deposition of materials layer by layer.
Surface model: a mathematical or digital representation of an object as a set of planar or curved surfaces or both, may or may not represent a closed volume.
N
Nesting: Placement of parts on the plane for optimal construction efficiency. Orientation, printing time printing time and material usage are common parameters to consider.
Example of nesting in Selective Laser Sintering - source Shapeways
O
Offset: this is the distance there is between the nozzle and the work surface.
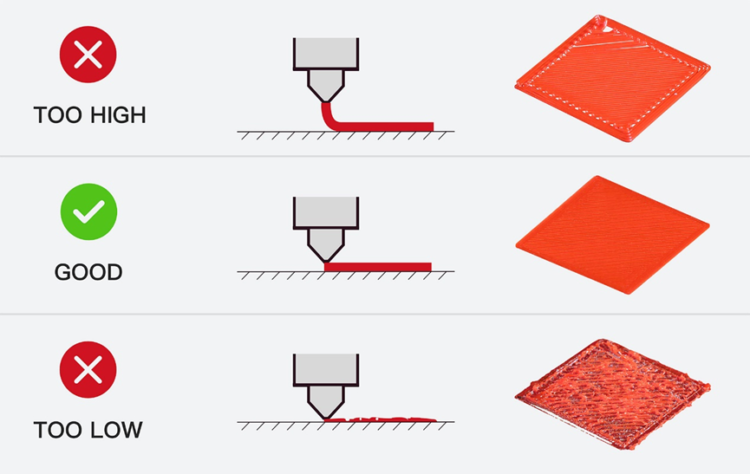
Guidelines for manually adjusting the value of offset Z based on the results of the first layer - source Raise3D
P
PDES (Product Data Exchange Specification): data exchange via STEP, a data exchange specification.
Printing plane: area on which 3D printing is carried out.
PLA: an acronym for polylactic acid, is a thermoplastic polymer commonly used in FDM 3D printing. It is derived from corn starch or sugar cane.
Polyjet: is a process similar to inkjet printing, it consists of jetting droplets of liquid photopolymer (in layers) onto a build tray that polymerize instantly by UV light.
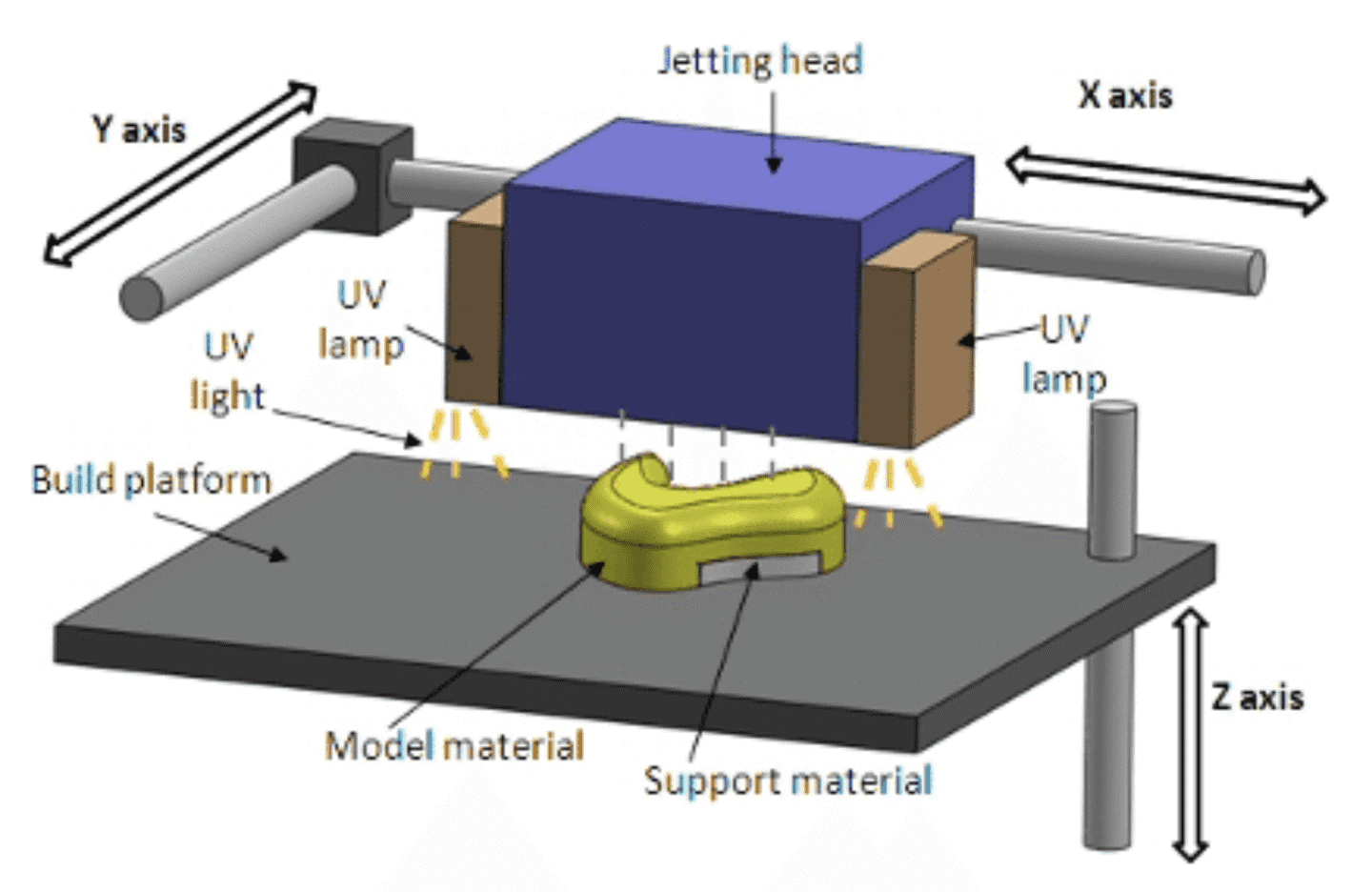
Polyjet technology-source Xometry
Post-processing: any act of improving the appearance or properties of materials in a 3D print after it has been printed. This covers a wide range of 3D printing processes that vary by technology (substrate removal, UV curing, heat treatment, sanding, tumbling, polishing, painting, etc.).
Additive manufacturing (additive manufacturing): process of fabricating a part by adding material in layers (often used as a synonymous term to 3D printing). Synonym: rapid prototyping.
Subtractive manufacturing: manufacturing by removing material (e.g., milling, drilling, grinding, carving, etc.) from a large solid to leave a desired shape. Contrary to additive manufacturing.
Prototype: a model built before mass production to test form, function, aesthetics, and interactions.
Melting point (melting point): the temperature at which a solid melts or turns into a liquid.
Do you need technical support?
If you need more information CONTACT US.
Follow our social media to keep up to date with the latest news!







